-
Home
-
About us
-
Products
-
Solutions
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact us
Leave Your Message

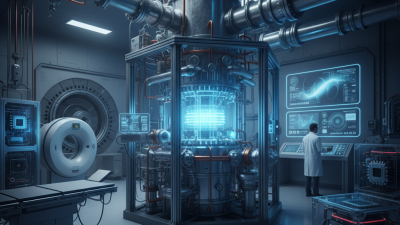
The Helium Super Cryogenic Refrigerator is a breakthrough in cooling technology. It operates at ultra-low temperatures, significantly enhancing performance in various applications. Researchers have developed it to address unique industrial needs, particularly in the fields of superconductivity and quantum computing.
However, understanding its intricate design and mechanics can be challenging. The refrigeration system relies on helium gas, which provides exceptional efficiency in heat removal. This technology enables researchers to reach temperatures that conventional systems cannot achieve. Despite these advancements, there are still hurdles in optimizing the operational aspects of the Helium Super Cryogenic Refrigerator.
The potential applications for this technology are immense, spanning from medical imaging to particle physics. Yet, not all implementations have been smooth. Users often encounter issues, leading to questions about reliability and efficiency. As we explore this technology, it is essential to reflect on areas for improvement while acknowledging its groundbreaking contributions.

Helium super cryogenic refrigeration technology is fascinating yet complex. At the core, it uses helium gas to achieve extremely low temperatures. This process is critical for many scientific and industrial applications. It plays a significant role in fields like particle physics and medical imaging.
One interesting aspect is the efficiency of this technology. Helium can reach temperatures below -250 degrees Celsius. This is vital for superconducting magnets. They require a cold environment to function effectively. However, managing liquid helium can be challenging. It evaporates quickly, which requires careful handling and monitoring.
Tips: If you're using this technology, always monitor the helium levels. This ensures optimal performance. Regular maintenance is also essential; it prevents unexpected breaks during critical operations. Lastly, ensure you have proper training. Working with cryogenic systems demands safety awareness and knowledge.
Moreover, the application of helium in cooling systems is not without flaws. The cost of helium can be high, affecting project budgets. Additionally, the supply of helium is limited. This situation prompts researchers to explore alternative cooling methods. It’s essential to weigh these factors against the benefits of cryogenic technology.

Helium super cryogenic refrigerators are crucial in various applications, especially in scientific research. Their design includes key components that optimize cooling efficiency. One essential part is the helium compressor, which pressurizes the helium gas. This gas is then cooled and expanded, allowing it to absorb heat from its surroundings. The process is highly efficient, with some systems reaching temperatures as low as 1.5 Kelvin.
Another critical component is the heat exchanger. It facilitates heat transfer between helium and the system, improving overall performance. Advanced designs can achieve a thermal efficiency of over 90%. However, the complexity of these components presents challenges. Maintenance can be costly, and component failure may lead to system downtime. It is essential to evaluate the long-term operational costs associated with these systems.
Moreover, the insulation material used plays a significant role in performance. High-quality vacuum insulation can reduce heat loss, enhancing energy efficiency. Research indicates that improved insulation can decrease energy consumption by as much as 30%. This reduction is vital for systems operating continuously in labs or hospitals. As technology advances, addressing these limitations could lead to even more effective solutions.

Helium-based cooling systems utilize unique principles of operation. They exploit the properties of helium, a noble gas, to achieve ultra-low temperatures. Helium remains liquid at extremely low temperatures, making it ideal for refrigeration needs. The cooling cycle generally involves compressing gas, cooling it down, and then expanding it to absorb heat. This process can create temperatures close to absolute zero.
Tips: Always ensure the helium's purity. Contaminants can reduce efficiency and damage components. Regular maintenance checks are crucial for optimal performance.
Cryogenic refrigerators often use a Joule-Thomson effect. As helium expands, it cools rapidly. The temperature drop is significant, making it suitable for various applications. However, sustaining these conditions can be technically challenging. Even slight fluctuations in pressure can affect performance.
Tips: Monitor pressure levels closely. Small changes can lead to substantial impacts. Pay attention to system insulation; any leaks will compromise cooling efficiency.
Helium super cryogenic refrigerators have unique applications in various industries. These systems chill materials to ultra-low temperatures, essential for numerous processes. In the medical field, they preserve biological samples effectively. Hospitals utilize these refrigerators to maintain the integrity of vaccines and sensitive drugs. This improves patient care significantly.
In the electronics industry, helium refrigerators are crucial for superconducting materials. They aid in developing high-performance magnets used in MRI machines. However, the operational costs can be high. This makes some companies hesitant to invest. Adequate planning and budgeting are necessary to justify these systems' expenses.
Furthermore, these refrigerators play a significant role in research facilities. They enable scientists to conduct experiments at temperatures near absolute zero. Yet, managing helium resources is a challenge. Helium scarcity raises concerns for long-term sustainability. Industries must reflect on more eco-friendly alternatives. Balancing innovation with environmental responsibility is essential in this field.
Helium cryogenic technology is evolving. Innovations in this field are shaping various industries. The demand for efficient cooling systems is increasing. Applications range from medical devices to telecommunications. Engineers are exploring new designs to enhance performance. They focus on reducing energy consumption while maximizing efficiency.
Future trends suggest advancements in materials and systems integration. Researchers aim to develop lightweight superconductors. These materials could revolutionize how we use cryogenic refrigerators. Improved thermal insulation methods are also on the horizon. This could lead to smaller and more efficient cooling units.
Tip: Regular maintenance can significantly improve the lifespan of cryogenic systems. Engineers should consider routine checks. Documentation of performance can help identify issues early. Emphasizing user training is vital as well. Lack of knowledge can lead to inefficient use of these advanced systems.