
-
Home
-
About us
-
Products
-
Solutions
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact us
Leave Your Message

The field of cryogenics has witnessed significant advancements, with the Helium Super Cryogenic Refrigerator emerging as a pivotal technology in various scientific and industrial applications. These sophisticated devices leverage the unique properties of helium at ultra-low temperatures to achieve remarkable cooling efficiency. In an era where high-performance cooling solutions are paramount for research, medical applications, and aerospace technologies, understanding the operational principles and benefits of Helium Super Cryogenic Refrigerators becomes essential.
Helium, as the primary working fluid in these refrigerators, offers superior thermal conductivity and a lower boiling point compared to other refrigerants, making it indispensable for achieving temperatures necessary for superconducting materials and quantum computing applications. The ability to maintain such extreme conditions not only enhances experimental outcomes in physics and engineering but also facilitates advancements in medical imaging techniques and particle accelerators.
This introduction will delve into the various applications and advantages of Helium Super Cryogenic Refrigerators, highlighting their transformative impact across multiple sectors. By exploring the intricacies of their functionality and the benefits they provide, we can better appreciate the role of these remarkable cooling systems in pushing the boundaries of modern science and technology.
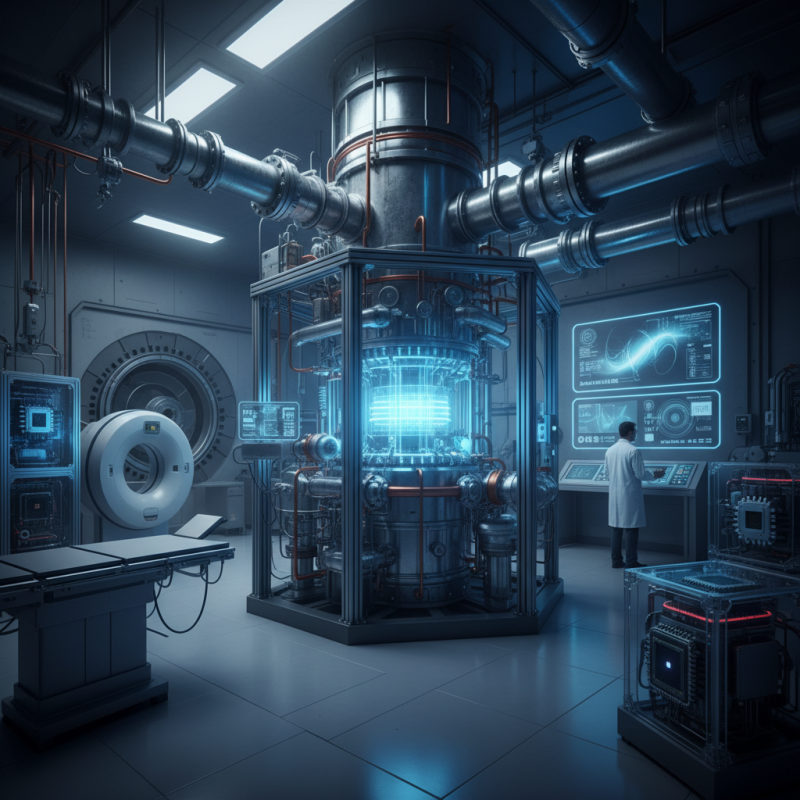

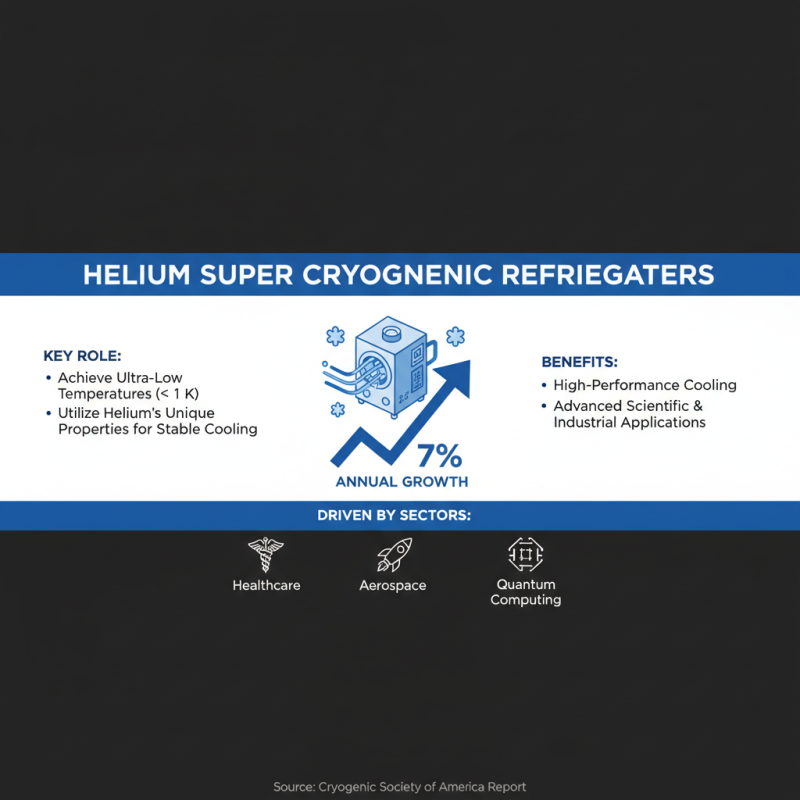
Helium super cryogenic refrigerators play a crucial role in various advanced scientific and industrial applications due to their ability to achieve ultra-low temperatures, typically below 1 K. These devices utilize helium as a coolant because of its unique thermal properties, which allow for efficient and stable refrigeration at cryogenic temperatures. According to a report by the Cryogenic Society of America, the demand for helium cryogenic systems is projected to grow by 7% annually, particularly driven by sectors such as healthcare, aerospace, and quantum computing. These applications greatly benefit from the high-performance cooling solutions offered by super cryogenic refrigerators.
One of the significant advantages of helium super cryogenic refrigerators is their efficiency in maintaining ultra-low temperatures necessary for the operation of superconductors and other cryogenic technologies. For instance, in the realm of particle physics, large particle accelerators depend on such refrigeration systems to maintain the superconducting magnets that are crucial for experiments. A study published in the Journal of Applied Physics highlights that advancements in cryogenic technology can lead to improved energy efficiency in cooling systems, potentially reducing operating costs by up to 30%. This efficiency not only benefits research institutions but also facilitates the development of innovative applications in materials science and quantum computing, marking a transformative era in technology.
Helium super cryogenic refrigerators operate on the principle of utilizing helium as a refrigerant to achieve extremely low temperatures essential for various applications. The cooling mechanism relies on helium’s unique properties, specifically its ability to remain in a liquid state at temperatures close to absolute zero. When helium is pressurized and subsequently allowed to expand, it cools significantly, employing the Joule-Thomson effect. This principle is pivotal in ensuring efficient cooling, as helium's low boiling point (approximately 4.2 K at atmospheric pressure) allows it to serve effectively in environments where traditional refrigerants fall short.
In recent years, the demand for advanced cooling technologies has surged, particularly in the fields of medical imaging and superconducting equipment. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global market for cryogenic equipment is expected to reach approximately $40 billion by 2025, with substantial growth driven by the need for enhanced cooling solutions in high-energy physics experiments and semiconductor manufacturing. Helium chillers provide a reliable and efficient means of achieving the ultra-low temperatures necessary for superconductivity, which is crucial for the operation of devices like MRI machines and particle accelerators. As a result, the integration of helium cooling technology stands as a significant advancement in both scientific research and industrial applications.
Helium super cryogenic refrigerators play a crucial role in various advanced applications, particularly in scientific research and industrial processes. These refrigerators operate at ultra-low temperatures, which are essential for superconducting materials used in particle accelerators, MRI machines, and fusion reactors. According to a report from the International Cryogenics Summit, the demand for these systems is projected to grow by over 10% annually as the need for efficient cooling solutions in high-energy physics experiments accelerates.
In the medical field, helium super cryogenic refrigerators enhance the performance and reliability of MRI and NMR systems by maintaining the superconducting magnets at optimal conditions. This is critical for achieving high-resolution imaging and diagnostic capabilities. Additionally, industries such as aerospace and electronics utilize these technologies to support research into new materials and the development of components that operate at cryogenic temperatures, which can improve energy efficiencies. The American Institute of Physics reported that advancements in cryogenic technology could lead to significant breakthroughs in energy conservation, potentially saving billions in operational costs across various sectors.
Helium has emerged as a pivotal element in cryogenic systems due to its unique properties, particularly its low boiling point of -269°C. This makes helium an ideal refrigerant for applications that require ultra-low temperatures, such as scientific research, medical imaging, and particle physics experiments. Utilizing helium in cryogenic refrigerators not only enhances cooling efficiency but also enables the development of larger and more powerful superconducting magnets, which are essential in technologies like MRI machines and particle accelerators.
One of the key advantages of helium in cryogenic systems is its high thermal conductivity. This property allows for rapid heat exchange, facilitating quicker cooling times and improved overall system performance. Additionally, helium remains in a gaseous state even at extremely low temperatures, which minimizes the risk of creating unwanted liquid phases that could hinder performance in sensitive equipment. Furthermore, the inert nature of helium prevents chemical reactions that could damage sensitive components, ensuring reliability and longevity in cryogenic applications.
Tips: When working with cryogenic systems, always ensure proper insulation is in place to optimize helium efficiency. Regular maintenance is crucial to detect any leaks promptly, as helium is a finite resource. Adequately training staff on safety protocols when handling cryogenic equipment can prevent accidents and ensure a safe working environment.
The demand for helium super cryogenic refrigerators is anticipated to grow significantly, driven by advancements in various sectors such as healthcare, electronics, and fundamental science research. According to industry reports, the global market for cryogenic refrigeration is expected to reach approximately $10.4 billion by 2025, highlighting an annual growth rate of about 8.5% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to the technology's efficiency in achieving ultralow temperatures, crucial for applications like MRI systems, superconducting materials, and high-energy physics experiments.
Innovations in cryogenic refrigeration technology continue to evolve, particularly in the areas of energy efficiency and cost reduction. Emerging designs, such as the integration of digital controls and high-performance heat exchangers, have shown promise in optimizing the cooling process and minimizing energy consumption. Additionally, advancements in materials science are paving the way for better insulation and reliability in cryogenic systems, which could lead to a reduction in overall maintenance costs and enhanced operational longevity. As these trends progress, helium cryogenic solutions are likely to play a pivotal role in supporting the next generation of scientific exploration and industrial applications.
This bar chart illustrates the various applications of Helium Super Cryogenic Refrigerators, showcasing their significant role in fields such as medical imaging, particle physics, and more. The percentages reflect the relative impact of these applications in the industry.





