
-
Home
-
About us
-
Products
-
Solutions
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact us
Leave Your Message

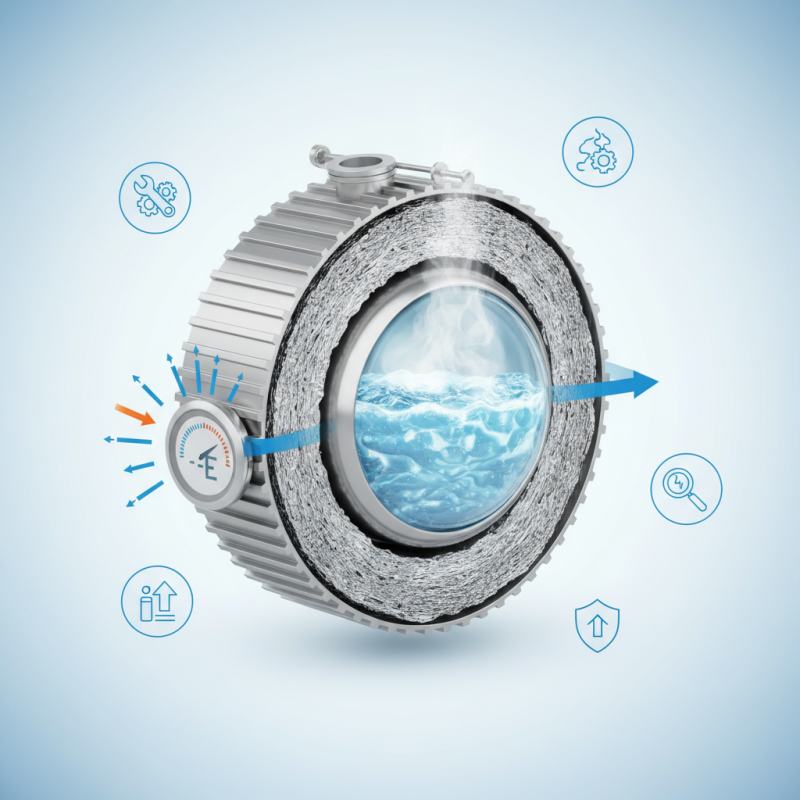
A Cryogenic Storage Tank is a crucial component in various industries. It is designed to store gases at extremely low temperatures. Typically, these tanks hold liquefied gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, and natural gas. The tank's structure ensures that the stored gases remain in liquid form. This process requires specialized insulation and temperature controls.
Understanding how a Cryogenic Storage Tank works can seem complex. The design prevents heat transfer and maintains low temperatures. Regular maintenance is essential for safety and efficiency. Without it, the tank may not perform well. Users need to check for any leaks regularly. These checks can help prevent accidents and ensure compliance with safety standards.
Despite its importance, not all tanks operate flawlessly. Some might encounter issues like thermal anomalies. Such problems can affect the storage of gases. Industry professionals must stay vigilant. They need to address any discrepancies quickly. This ongoing need for improvement highlights the importance of training and knowledge in handling Cryogenic Storage Tanks.

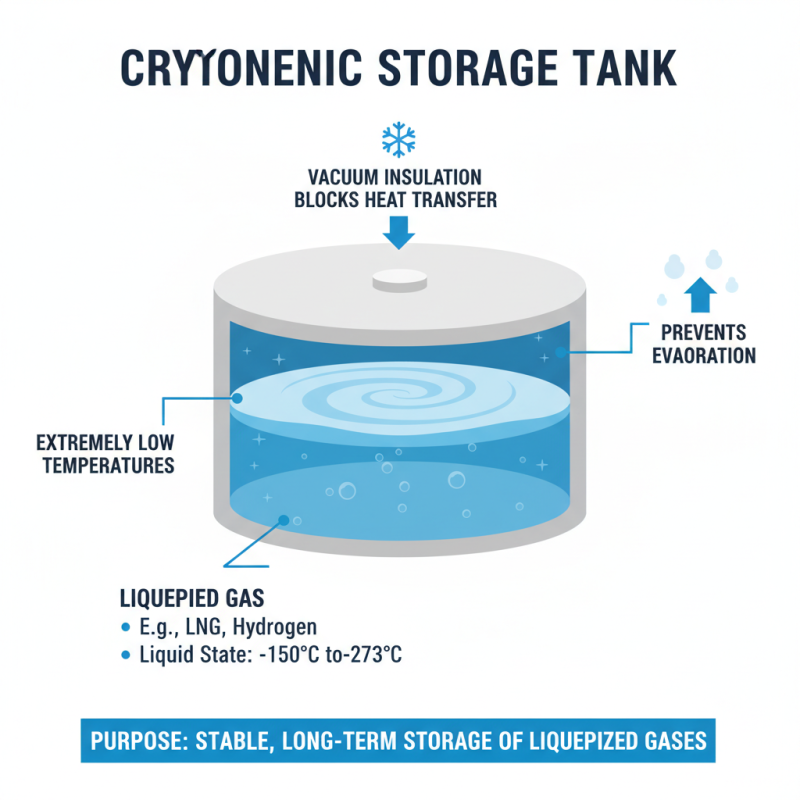
A cryogenic storage tank is designed to hold materials at extremely low temperatures. These temperatures often range from -150°C to -273°C. The purpose is to keep gases like liquefied natural gas or hydrogen in a liquid state. The tank's insulation is critical. It prevents heat from entering and keeps the contents stable.
When using a cryogenic tank, safety is key. Ensure that the tank is made from compatible materials. Some materials can become brittle in low temperatures. Inspect the tank regularly for any signs of wear or damage. Small cracks can lead to massive leaks.
Tips: Always wear protective gear when handling cryogenic materials. Follow.
Ventilation is essential. It helps prevent gas accumulation, which can be dangerous. Have a gas detection system nearby. It provides early warnings of any leaks.
In conclusion, a cryogenic storage tank plays a crucial role in various industries. Understanding its design and operation is vital for safety and efficiency. Regular maintenance can prevent potential issues.
Cryogenic storage tanks are crucial for containing liquefied gases at extremely low temperatures. Understanding the physics behind cryogenic liquids is essential for efficient storage. At -150°C or lower, gases become liquids, allowing for more compact storage. Liquid nitrogen and liquid helium are common examples. These cryogenic liquids play vital roles in various industries, including aerospace and medical fields.
The process of storing cryogenic liquids involves keeping them at specific temperatures and pressures. A professional report from the American Cryogenics Association states that tank insulation can reduce energy loss by up to 85%. The vacuum insulation used in these tanks prevents heat transfer. However, the design must account for potential challenges. Risk of venting or pressure build-up requires regular monitoring.
Cryogenic storage tanks come with their own set of complexities. Operators must ensure proper maintenance to avoid leaks and failures. A report by the European Industrial Gases Association mentions that approximately 10% of cryogenic plants face operational inefficiencies. This highlights the importance of ongoing training and technology updates. Ensuring safety and efficiency demands constant vigilance in handling these materials.
This chart represents the storage capacity of various cryogenic liquids in liters. As seen, oxygen has the highest storage capacity, followed by nitrogen and argon, showcasing the differences in requirements and usability of these cryogenic liquids in industrial applications.

Cryogenic storage tanks are essential for storing liquefied gases at extremely low temperatures. Understanding their key components can shed light on their functionality. These tanks have an outer casing, typically made from stainless steel, which ensures durability. Inside, there’s a vacuum space that minimizes heat transfer. This vacuum is crucial; it keeps the contents stable and safe.
The insulation materials used are also vital. They prevent thermal conduction, ensuring the contents remain at the desired low temperatures. Some tanks also have safety valves. These help regulate internal pressure. If pressure builds up, the valves vent the gas safely. It’s a simple yet critical feature that protects against accidents.
Another noteworthy component is the filling and withdrawal system. This system allows for easy access to the stored gas. However, it requires proper maintenance. Regular inspection can prevent leaks. Neglecting this can lead to significant hazards. Users must be aware of the importance of these components. A lack of attention to detail could result in serious issues.
Cryogenic storage tanks are essential for handling liquefied gases. They are built to withstand extremely low temperatures, often below -150 degrees Celsius. Safety standards are crucial in this field. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) sets rigorous guidelines for these structures. Compliance ensures they can handle the intense pressure that arises during gas storage.
In 2021, a report by the International Institute of Refrigeration noted a rising concern around cryogenic safety. Over 25% of reported incidents involved improper handling or poor maintenance. Regular inspections are critical. They can prevent leaks or worse, catastrophic failures. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) emphasizes training for all personnel. Understanding the risks and proper procedures can reduce accidents significantly.
Moreover, many facilities face challenges in adhering to regulations. Some lack adequate resources for safety equipment. A recent survey highlighted that less than 40% of facilities invest enough in safety gear. This gap often results in overlooked hazards. Maintaining high standards is not just about regulations; it's about ensuring safety for all involved.
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Vertical, Horizontal, Mobile |
| Capacity | From 5,000 liters to over 200,000 liters |
| Materials | Stainless steel, Aluminum |
| Insulation | Vacuum or Multi-layer insulation |
| Safety Standards | ASME, PED, ISO |
| Common Uses | Storage of Liquid Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon |
| Temperature Range | -196°C to -253°C |
| Regulatory Bodies | OSHA, EPA, NFPA |
Cryogenic tanks play a crucial role in various sectors. In the medical industry, they store liquid nitrogen for preserving biological samples. Hospitals rely on these tanks for organ preservation. The low temperatures prevent cells from deteriorating. However, maintaining these temperatures requires careful monitoring and regular maintenance. Small issues can lead to significant losses.
The aerospace industry also benefits greatly from cryogenic technology. Liquid fuels, such as liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen, are stored in cryogenic tanks for rocket propulsion. The efficiency gained is significant, but the risk of leaks looms large. Engineers must ensure leak detection systems are infallible. The margin for error is slim when launching missions.
In the food industry, cryogenic tanks assist in the freezing process. Foods are flash-frozen to retain nutrients and flavor. Although effective, there is always a potential for contaminants if tanks aren't properly sanitized. Staff must be trained rigorously. Each use holds the promise of freshness but comes with a caveat that shouldn't be ignored.





