
-
Home
-
About us
-
Products
-
Solutions
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact us
Leave Your Message

When it comes to storing materials that require extremely low temperatures, selecting the right cryogenic containers is crucial for ensuring safety, efficiency, and preservation. Cryogenic containers are specially designed vessels that maintain and protect their contents under such demanding conditions. Whether you are working in sectors like biomedical research, aerospace, or industrial applications, understanding the different types and specifications of cryogenic containers can significantly impact the integrity of your stored materials.
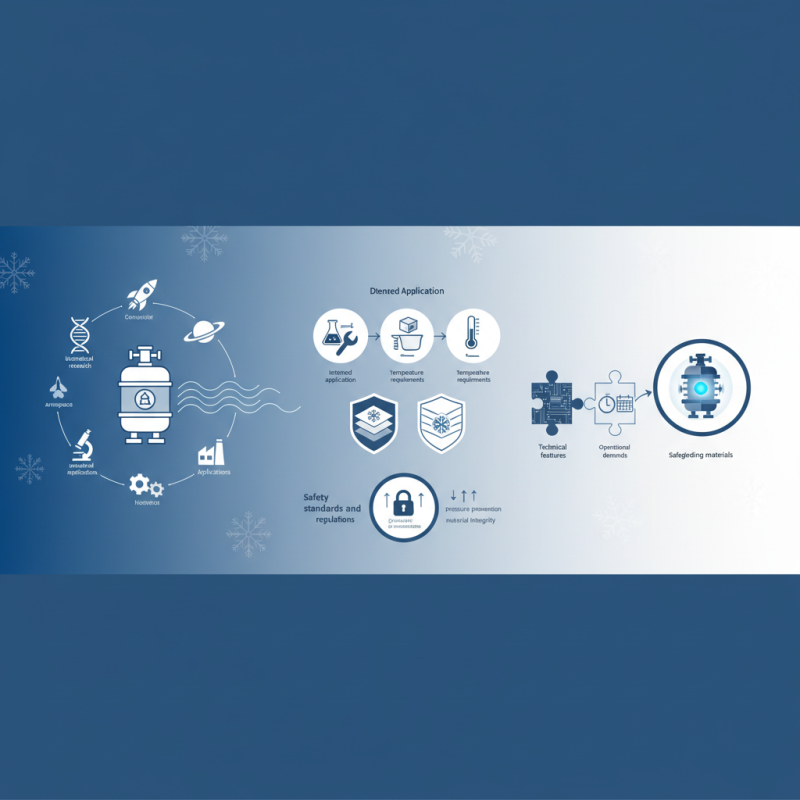
In the process of choosing the appropriate cryogenic containers, several factors must be considered. These include the intended application, the volume of material to be stored, and the specific temperature requirements. The material construction and insulation properties of the containers also play a vital role in maintaining cryogenic temperatures while minimizing energy loss. Furthermore, ensuring that the containers meet safety standards and regulations is essential in preventing hazardous situations related to pressure build-up and material degradation.
Ultimately, making an informed decision about cryogenic containers involves evaluating both the technical features and the operational demands of your storage needs. By understanding these elements, you can select the most suitable cryogenic containers that will safeguard your valuable materials while delivering optimal performance in a range of applications.

When selecting cryogenic containers for your storage needs, several key factors should be taken into consideration. Firstly, the intended use of the container plays a critical role. Different applications require varying capacities, insulation techniques, and safety features. For instance, if you are storing biological samples, ensure the container is designed to maintain consistent low temperatures suitable for preserving the integrity of the samples over time.
Another important factor is the material of the cryogenic container. Containers made from durable materials such as aluminum or stainless steel provide better insulation and reliability during storage. They are also more resistant to cracking and can withstand the extreme temperatures associated with cryogenic storage. When assessing your options, always check the specifications regarding temperature ranges and vacuum insulation efficiency, as these directly affect the container's performance.
**Tips:** Always calculate the total volume of materials you plan to store before choosing a container size. This helps avoid overfilling and ensures safe storage conditions. Additionally, consider the ease of handling; containers with ergonomic designs facilitate better management, especially when it comes to transporting them within a facility. Regular maintenance checks for wear and tear should also be part of your routine to safeguard against potential leaks and other hazards.
When selecting the right cryogenic containers for your storage needs, it's essential to understand the primary types available, each designed for specific applications. Dewars are perhaps the most common form of cryogenic containers. They consist of double-walled vacuum insulation, which significantly reduces heat transfer, keeping the contents at very low temperatures. Dewars are ideal for short-term storage and transportation of liquefied gases such as nitrogen or helium, allowing laboratory and medical facilities to maintain these substances with minimal evaporation losses.
Vacuum flasks serve a similar purpose to Dewars but are typically smaller and more suitable for individual use or smaller scale applications. These flasks leverage the same vacuum insulation technology to keep liquids cryogenically cold, making them perfect for portable storage of small quantities of cryogenic materials. This type of container is often used in research environments where small samples need to be preserved at low temperatures over brief periods.
For larger-scale storage and long-term usage, cryogenic tanks are the go-to solution. These tanks are built with robust insulation and can hold significant volumes of cryogenic liquids for extended durations. They are commonly used in industrial applications where bulk amounts of liquid nitrogen or oxygen are required, providing safe and efficient storage while ensuring minimal energy loss. Each type of cryogenic container has its specific advantages, making it crucial to assess your storage needs carefully when making a selection.

When selecting cryogenic containers for storage, understanding the material specifications is crucial. The choice between metal, plastic, and glass containers significantly influences performance and safety. According to a market analysis by the Cryogenic Society of America, metal containers, particularly those made from aluminum and stainless steel, are the most commonly used in cryogenic applications due to their durability and resistance to extreme temperatures. These materials maintain structural integrity in temperatures as low as -196°C, making them ideal for storing liquefied gases like nitrogen and oxygen.
In contrast, plastic cryogenic containers, typically made from polyethylene or polypropylene, provide excellent insulation properties. They are lightweight and can be effective for short-term storage; however, they may not withstand the same extreme temperatures and pressures as metal ones. A report by the National Institute of Standards and Technology highlights that while plastics can be a cost-effective alternative, their use should be limited to specific applications where prolonged exposure to cryogenic conditions is not a concern. Glass containers, while providing chemical inertness and clarity for visibility, tend to be more fragile and impractical for high-volume storage needs, making them less popular in professional settings. The choice of container not only hinges on material properties but also on the intended use and storage duration of cryogenic substances.
When selecting cryogenic containers, temperature maintenance and insulation are crucial factors that directly impact the efficacy of storage solutions. According to a report from the Cryogenic Society, maintaining optimal temperature conditions is essential for preserving the physical and chemical properties of cryogenic fluids. For instance, liquid nitrogen requires storage at temperatures below -196°C. Insulation materials like vacuum barriers, multi-layer insulation (MLI), and materials with low thermal conductivity are vital in minimizing heat transfer, which can lead to loss of cryogenic liquids and potential safety hazards.
Moreover, proper insulation not only preserves the integrity of stored cryogenic materials but also enhances the efficiency of storage systems. A study published by the American Institute of Physics highlights that well-insulated cryogenic systems can reduce boil-off rates by up to 50%, significantly lowering operational costs. Therefore, when choosing cryogenic containers, it is imperative to evaluate insulation properties and determine their suitability based on storage duration and environmental conditions. Selecting containers with robust insulation technology ensures reliable temperature maintenance, thereby safeguarding the material stored within from degradation and maximizing resource efficiency.
This chart shows the average temperature maintenance efficiency of various cryogenic containers over a 24-hour period. The efficiency is measured in degrees Celsius maintained below the ambient temperature.
When selecting cryogenic containers, it’s crucial to adhere to the established safety regulations and standards to mitigate risks associated with the storage of cryogenic materials. Organizations such as the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) provide guidelines that cover the design and operation of these containers. Compliance with these regulations not only ensures the safety of personnel but also helps to maintain the integrity of the stored substances, preventing accidents and harmful exposures.
In addition to following the guidelines from regulatory bodies, it’s important to regularly inspect and maintain cryogenic containers. This includes checking for signs of wear, ensuring that valves and seals are functioning properly, and verifying the insulation properties to minimize heat transfer. Staff training on emergency procedures and the correct handling of cryogenic materials is also a key component of safety. By staying informed about the latest standards and investing in necessary training and maintenance practices, organizations can safeguard their operations and enhance the efficacy of their cryogenic storage solutions.





