
-
Home
-
About us
-
Products
-
Solutions
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact us
Leave Your Message

As the world increasingly shifts towards sustainable energy solutions, the demand for efficient hydrogen storage and transportation technologies has never been more critical. Among these technologies, the Big Capacity Hydrogen Liquefier stands out as a transformative innovation poised to address the challenges associated with hydrogen logistics. Due to its ability to cool and liquefy large volumes of hydrogen, this advanced system not only enhances the feasibility of hydrogen as a clean energy source but also plays a pivotal role in scaling up hydrogen applications across various industries.
In recent years, significant advancements have been made in the design and operational efficiency of Big Capacity Hydrogen Liquefiers. These innovations are driven by the need to reduce energy consumption, operational costs, and environmental impact, thus paving the way for more sustainable solutions in hydrogen utilization. Moreover, the exploration of new materials and technologies in liquefaction processes is set to expand the capabilities of these systems, leading to increased production rates and improved safety measures.
Looking toward the future, the prospects for Big Capacity Hydrogen Liquefiers appear promising. As nations strive to meet their renewable energy targets and carbon reduction goals, the role of hydrogen in the energy mix is likely to grow, underscoring the importance of continued innovation in liquefier technology. This exploration into the trends and future potential of Big Capacity Hydrogen Liquefiers will shed light on their significance in the evolving landscape of global energy solutions.

Hydrogen liquefaction technology plays a vital role in the emerging hydrogen economy, enabling the storage and transportation of hydrogen in a compact and efficient manner. The process of converting hydrogen gas into a liquid involves cooling it to extremely low temperatures, typically around -253°C. This transformation reduces the volume of hydrogen by approximately 800 times, facilitating its movement through pipelines and tankers. According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), the global hydrogen market is projected to grow significantly, reaching an estimated 622 million tonnes by 2040, making advancements in liquefaction technology increasingly important.
The importance of hydrogen liquefaction cannot be understated, especially as we transition towards sustainable energy sources. Enhanced liquefaction technologies can improve efficiency and reduce costs, crucial for the competitiveness of hydrogen relative to other energy carriers. Recent studies indicate that innovations in cryogenic systems and compressor designs can potentially lower liquefaction energy consumption by 30%, which is a game-changer in terms of operational costs for hydrogen liquefiers.
Tips: When considering investment in hydrogen liquefaction, be sure to analyze the technology's energy efficiency and associated operational costs. Staying updated on industry trends and research can also provide insights into potential future innovations that could impact market dynamics. Regularly consulting reports from recognized energy organizations can help identify key performance indicators to guide strategic decisions in this rapidly evolving sector.
Recent advancements in big capacity hydrogen liquefiers have significantly transformed the hydrogen production landscape. These innovations are driven by the increasing demand for hydrogen as a clean energy source, which necessitates more efficient and scalable liquefaction processes. Significant breakthroughs include the development of advanced cryogenic systems that optimize energy consumption and enhance liquefaction efficiency, allowing for more sustainable operations. Additionally, new materials and technologies are being explored to improve insulation and reduce heat loss, which is critical in maintaining low temperatures during the liquefaction process.
Tips for businesses looking to invest in hydrogen liquefaction: firstly, consider the energy sources for your liquefaction process to ensure it aligns with sustainability goals. Utilizing renewable energy can enhance the overall carbon footprint of hydrogen production. Secondly, keep abreast of regulatory environments that may affect the deployment of liquefaction technologies, as this can influence operational costs and market expansion. Finally, collaborating with research institutions can provide insights into the latest innovations and help integrate cutting-edge technologies into your operations, fostering continuous improvement and competitive advantage.
| Feature | 2023 Innovations | Efficiency (%) | Production Capacity (ton/day) | Future Prospects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cryogenic Cooling | Improved heat exchange efficiency | 95 | 40 | Expected increase to 60 tons/day by 2025 |
| Hydrogen Purity | Advanced filtration systems | 99.999% | 30 | Higher purity target for fuel cell applications |
| Energy Recovery | New turbine technologies | 87 | 50 | Further improvements expected |
| Modularity | Scalable designs for flexibility | N/A | 20-100 | Adaptable to growing demands |
| Sustainability | Integration with renewable energy | 78 | 15 | Increased reliance on green hydrogen |
The landscape of hydrogen liquefaction is rapidly evolving, driven by several key trends that promise to shape its future. One significant trend is the advancement of cryogenic technology, which enhances the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of hydrogen liquefaction processes. Innovations in materials science have led to the development of more effective insulation and energy-recovery systems, minimizing energy losses during hydrogen cooling and liquefaction. These technological improvements not only lower operational costs but also contribute to the sustainability of hydrogen as a clean energy source.
Another pivotal trend is the integration of renewable energy sources into the hydrogen liquefaction process. By utilizing excess energy from wind or solar power, facilities can generate hydrogen through electrolysis and subsequently liquefy it with a lower carbon footprint. This synergy between renewable energy and hydrogen production positions liquefied hydrogen as a viable solution for energy storage and transport, aligning with global efforts to transition to cleaner energy systems.
Additionally, the push for standardized liquefaction processes is emerging as a crucial driver, promoting scalability and interoperability that could streamline the supply chain for hydrogen across various sectors.
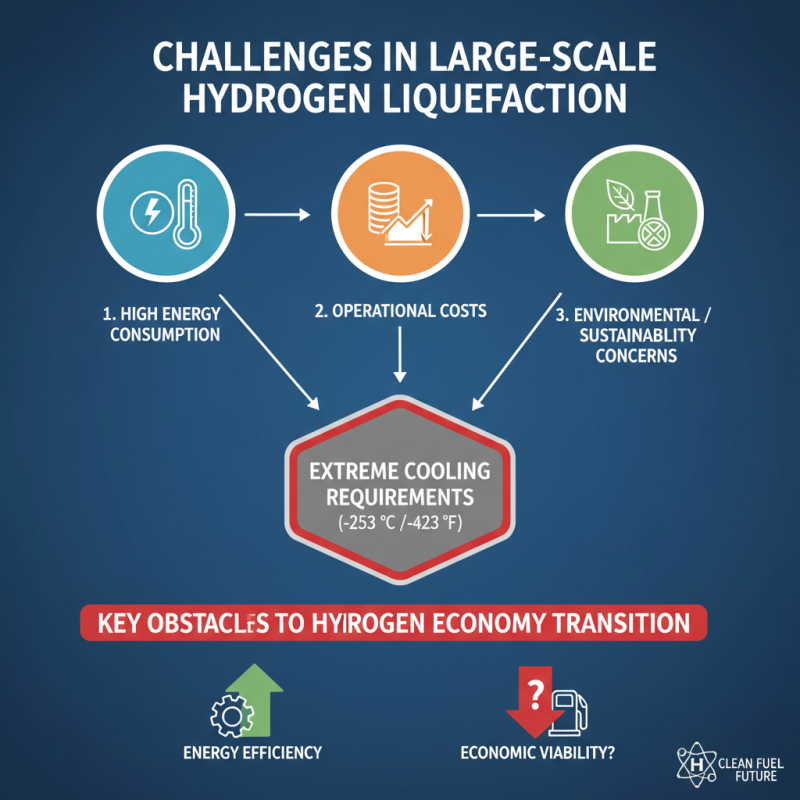
The development of large-scale hydrogen liquefiers faces several significant challenges that must be addressed to accelerate the transition towards a hydrogen economy. One of the primary obstacles is the high energy consumption associated with the liquefaction process. The cooling requirements to reach the extremely low temperatures necessary for hydrogen liquefaction demand substantial energy input, often resulting in higher operational costs and environmental concerns. This dependence on energy efficiency not only affects economic viability but also raises questions about the overall sustainability of hydrogen as a clean fuel option.
Another challenge lies in the materials and technologies required for constructing liquefiers capable of handling large volumes of hydrogen. The design must ensure safety and durability under extreme conditions, which necessitates advanced materials that can withstand low temperatures and hydrogen embrittlement. Research into innovative materials and manufacturing methods is critical, yet the pace of development often lags behind the market's growing demand for hydrogen solutions. Furthermore, ensuring scalability while maintaining high performance presents an additional hurdle that developers must overcome to meet future hydrogen supply needs effectively. Addressing these challenges through collaborative research and investment in technology will be essential for unlocking the full potential of large-scale hydrogen liquefaction.
As the world increasingly focuses on the transition to sustainable energy sources, hydrogen liquefaction stands out as a crucial technology with significant market potential. The ability to store and transport hydrogen in liquid form opens up new avenues for its use as a clean energy carrier. This innovation is vital for regions lacking extensive pipeline networks, enabling the global distribution of hydrogen to support various applications, from fuel cells to industrial processes. The demand for hydrogen as a clean fuel is expected to grow exponentially, driven by decarbonization efforts across multiple sectors, including transportation and manufacturing.
The environmental impact of hydrogen liquefaction is equally noteworthy. By integrating renewable energy sources into the liquefaction process, the carbon footprint associated with hydrogen production can be significantly reduced. Moreover, advances in cryogenic technology and energy efficiency can further mitigate environmental effects. As the industry progresses, the focus will likely shift towards developing sustainable practices that enhance the viability of hydrogen as a cornerstone in the global energy landscape. Stakeholders are increasingly recognizing the necessity of aligning economic growth with ecological preservation, placing hydrogen liquefaction at the forefront of future energy solutions.





